An occupational therapy driving assessment is a comprehensive evaluation of an individual’s ability to drive safely, focusing on physical, cognitive, and visual abilities. Conducted by certified professionals, it ensures safe mobility and independence, addressing medical or functional limitations that may impact driving skills. This assessment is crucial for promoting safe and independent mobility, especially for seniors or individuals with disabilities, helping to determine fitness-to-drive and recommend necessary interventions or vehicle modifications. The process typically includes both off-road and on-road components, ensuring a thorough understanding of the individual’s driving capabilities and needs.

Key Components of an Occupational Therapy Driving Assessment
A driving assessment involves two main components: an off-road evaluation and an on-road test. The off-road assessment evaluates vision, motor skills, and cognitive abilities, while the on-road test observes practical driving behaviors and safety. These components ensure a holistic evaluation of an individual’s driving capabilities, addressing physical, visual, and cognitive limitations to determine fitness-to-drive and recommend appropriate interventions or adaptations.
2.1. Off-Road Assessment
The off-road assessment is the initial stage of the driving evaluation, focusing on identifying physical, cognitive, and visual limitations that may impact driving. It includes a review of medical and driving history, vision testing, and evaluations of motor skills, perception, and cognitive abilities. Standardized tools, such as the Assessment of Motor and Process Skills (AMPS), are often used to assess functional abilities. This phase helps determine whether an on-road test is appropriate and highlights areas needing intervention or adaptation.
- Evaluation of vision, cognition, and motor skills.
- Review of medical and driving history.
- Use of standardized assessment tools.
2.2. On-Road Assessment
The on-road assessment evaluates an individual’s ability to drive safely in real-world conditions, conducted in a dual-controlled vehicle. A qualified instructor observes driving behaviors, including vehicle control, navigation, and adherence to traffic rules. This phase focuses on practical skills, such as turning, braking, and merging, to assess situational awareness and decision-making. The results help determine driving competence and identify areas requiring intervention or adaptive equipment.
- Evaluation of practical driving skills.
- Assessment of situational awareness and decision-making.
- Use of a dual-controlled vehicle for safety.
The Role of Occupational Therapists in Driving Assessments
Occupational therapists evaluate an individual’s driving abilities, identifying physical, cognitive, and visual limitations. They provide personalized recommendations to enhance safe driving practices and independence.
3.1. Specialized Training and Certification
Occupational therapists undergo specialized training to assess driving abilities, often earning certifications like a Certified Driving Rehabilitation Specialist (CDRS). This expertise enables them to evaluate physical, cognitive, and visual skills, ensuring accurate fitness-to-drive determinations. They utilize standardized tools such as the Rookwood Driving Battery (RDB) and Assessment of Motor and Process Skills (AMPS) to provide evidence-based recommendations for safe and independent mobility.
3.2. Use of Evidence-Based Tools and Resources
Occupational therapists employ evidence-based tools like the Rookwood Driving Battery (RDB) and Assessment of Motor and Process Skills (AMPS) to evaluate driving abilities. These resources assess vision, cognition, and motor skills, ensuring accurate fitness-to-drive determinations. Standardized assessments guide recommendations for safe driving practices, vehicle modifications, or rehabilitation programs, promoting independence and mobility while adhering to medical guidelines and legal requirements.

Functional Abilities Assessed in Driving Evaluations
Driving evaluations assess vision, motor, and cognitive abilities, ensuring safe control of a vehicle. These skills are critical for navigating roads effectively and maintaining driver safety.
4.1. Vision and Perceptual Skills
Vision and perceptual skills are critical in driving assessments, focusing on visual acuity, field of vision, depth perception, and reaction time. These abilities enable drivers to detect hazards, judge distances, and navigate safely. Occupational therapists evaluate how well individuals process visual information to make timely driving decisions. Any deficits in these areas may require corrective measures, such as glasses or adaptive equipment, to ensure safe and effective driving capabilities. Accurate visual processing is essential for road safety and independence.
4.2. Motor and Physical Abilities
Motor and physical abilities are essential for safe driving, including strength, coordination, and reaction time. Occupational therapists assess an individual’s ability to perform driving-related tasks, such as steering, braking, and accelerating. Physical limitations, such as reduced neck mobility or leg strength, are evaluated to determine their impact on driving performance. Adaptive equipment or rehabilitation may be recommended to address physical challenges, ensuring safe and effective control of a vehicle.
4.3. Cognitive and Executive Functioning
Cognitive and executive functioning are critical for driving, including attention, memory, decision-making, and reaction time. Occupational therapists assess abilities like processing traffic signals, navigating intersections, and maintaining focus. Impairments in these areas may indicate the need for interventions or adaptive strategies. Standardized tools evaluate cognitive skills, ensuring safe driving practices and recommending appropriate support or rehabilitation to enhance independence and mobility behind the wheel.

The Process of Conducting a Comprehensive Driving Evaluation
A comprehensive driving evaluation involves pre-assessment screening, on-road testing, and post-assessment feedback, ensuring a thorough assessment of driving abilities and safety.
5.1. Pre-Assessment Screening and Preparation
The pre-assessment phase involves gathering medical history, vision testing, and reviewing legal requirements. Clients prepare by bringing necessary documents, such as medical clearance. Occupational therapists ensure clients understand the process and expectations. This step identifies potential risks and ensures safety during the on-road evaluation. Proper preparation is crucial for accurate assessment of driving abilities and fitness-to-drive determination, aligning with legal and medical standards to promote safe mobility outcomes.
5.2. On-Road Testing and Observation
The on-road assessment involves evaluating driving skills in real-world conditions. Conducted in a dual-controlled vehicle, it observes navigation, traffic rule adherence, and vehicle control. Occupational therapists assess reaction time, decision-making, and ability to manage various road scenarios. This phase provides insights into practical driving abilities, ensuring safety and independence. Observations are documented to inform recommendations for safe mobility, further training, or necessary vehicle modifications.
5.3. Post-Assessment Feedback and Recommendations
Following the evaluation, occupational therapists provide detailed feedback and recommendations. This includes a summary of strengths, areas for improvement, and strategies to enhance driving safety. Recommendations may involve specialized vehicle modifications, rehabilitation programs, or restrictions on driving privileges. The feedback is often documented in a PDF report, ensuring clarity and guidance for individuals, families, and healthcare providers to support safe and independent mobility.
Tools and Resources Used in Driving Assessments
Occupational therapy driving assessments utilize standardized tools like AMPS and RDB to evaluate motor, cognitive, and visual skills, ensuring accurate and evidence-based evaluations for safe driving.
6.1. Assessment of Motor and Process Skills (AMPS)
The Assessment of Motor and Process Skills (AMPS) is a standardized tool used by occupational therapists to evaluate an individual’s ability to perform daily living tasks. It focuses on motor skills, such as coordination and dexterity, and process skills, like task planning and execution. In driving assessments, AMPS helps identify functional abilities critical for safe driving, ensuring accurate and evidence-based recommendations for fitness-to-drive evaluations.
6.2. Rookwood Driving Battery (RDB)
The Rookwood Driving Battery (RDB) is a standardized screening tool used by occupational therapists to assess cognitive and perceptual skills essential for driving. It evaluates attention, memory, and visual perception, providing insights into an individual’s ability to process information while driving. Suitable for various conditions, such as stroke or dementia, the RDB helps identify driving-related strengths and weaknesses, supporting safe and informed fitness-to-drive determinations as part of a comprehensive driving evaluation.
6.3. Other Standardized Evaluation Tools
Beyond the AMPS and RDB, other standardized tools are used in occupational therapy driving assessments to evaluate specific abilities. These include cognitive and visual assessments, as well as tools tailored for conditions like stroke or dementia. Evidence-based instruments help occupational therapists identify strengths, weaknesses, and the need for interventions. These tools play a critical role in ensuring safe mobility and informed decision-making during the driving evaluation process.

Legal and Medical Considerations in Driving Assessments
Occupational therapy driving assessments must adhere to legal and medical guidelines, ensuring compliance with fitness-to-drive standards. Medical clearance is often required, and legal obligations may involve reporting unfit drivers. These considerations protect public safety and ensure ethical practices in determining driving eligibility.
7.1. Medical Clearance and Fitness-to-Drive Guidelines
Medical clearance is a critical step in occupational therapy driving assessments, ensuring individuals meet fitness-to-drive standards. Occupational therapists use evidence-based tools to evaluate vision, cognition, and motor skills, adhering to medical guidelines. This process helps determine safe driving capabilities and may require input from healthcare professionals. Clear guidelines ensure ethical and informed decisions, balancing individual independence with public safety, and addressing any medical conditions that could impact driving ability.
7.2. Legal Requirements and Reporting Processes
Occupational therapy driving assessments must comply with legal standards, ensuring public safety and accountability. Therapists are legally obligated to report individuals who may pose a risk on the road. Standardized reporting processes and documentation are used to inform licensing authorities. Confidentiality is maintained while adhering to legal guidelines, balancing individual rights with community safety. This ensures ethical and lawful decision-making in determining fitness-to-drive status.
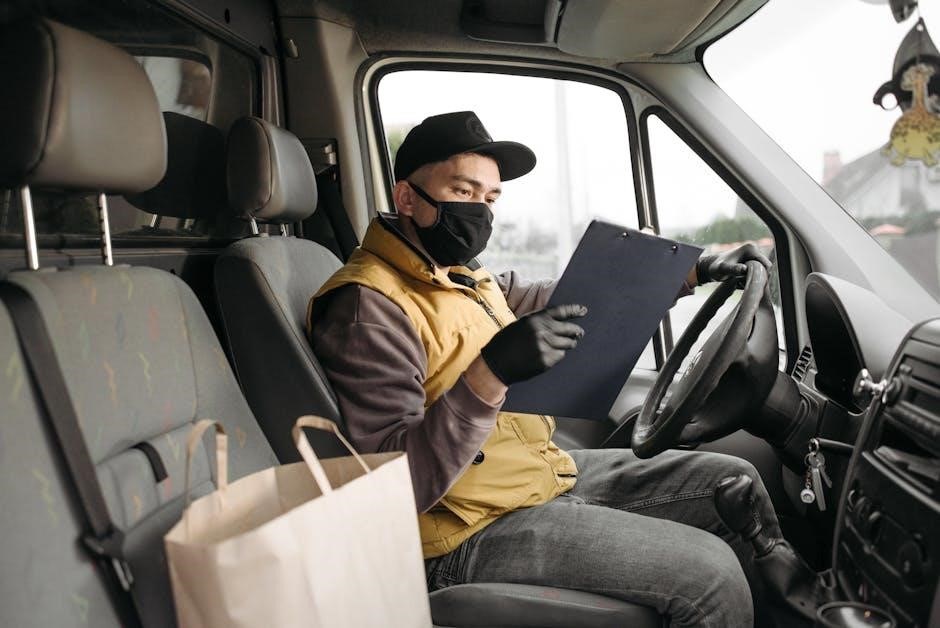

Benefits of Occupational Therapy Driving Assessments
Occupational therapy driving assessments promote safe mobility, independence, and confidence for individuals with disabilities or medical conditions, enabling them to maintain or regain driving abilities effectively.
8.1. Promoting Safe and Independent Mobility
Occupational therapy driving assessments play a vital role in promoting safe and independent mobility for individuals with medical or functional limitations. By identifying physical, cognitive, or visual challenges, these evaluations ensure drivers can operate vehicles safely. Personalized recommendations, such as adaptive equipment or rehabilitation programs, empower individuals to maintain independence while reducing risks. This approach not only enhances road safety but also boosts confidence and overall quality of life for drivers.
8.2. Rehabilitation and Return-to-Driving Programs
Rehabilitation and return-to-driving programs are tailored to help individuals regain driving abilities after medical or functional challenges. These structured programs focus on improving physical, cognitive, and visual skills through targeted exercises and simulations. Occupational therapists work collaboratively with drivers to address deficits, build confidence, and ensure safe return to driving. The goal is to maximize independence while prioritizing road safety and overall mobility.

Specialized Services and Support
Specialized services include customized vehicle modifications and adaptive equipment to support safe driving. These services address specific needs, ensuring individuals with disabilities or impairments can drive independently and confidently.
9.1. Disability-Specific Driving Assessments
Disability-specific driving assessments are tailored to evaluate individuals with unique needs, such as physical, cognitive, or visual impairments. Occupational therapists use standardized tools like the Rookwood Driving Battery and Assessment of Motor and Process Skills (AMPS) to assess functional abilities. These assessments provide customized recommendations for adaptive equipment and vehicle modifications, ensuring safe and independent driving. They also address rehabilitation goals and promote mobility for individuals with lifelong or acquired disabilities.
9.2. Customized Vehicle Modifications and Adaptive Equipment
Customized vehicle modifications and adaptive equipment are essential for individuals with specific disabilities, enabling safe and independent driving. Occupational therapists recommend tailored solutions, such as steering aids, pedal extensions, or seat adjustments, based on assessment findings. These modifications enhance mobility and accessibility, addressing physical or cognitive limitations. Adaptive equipment ensures proper positioning, control, and safety, allowing individuals to operate a vehicle confidently and maintain their independence on the road.
Occupational therapy driving assessments are vital for ensuring safe and independent mobility, particularly for individuals with disabilities or medical conditions. These evaluations, conducted by skilled professionals, address physical, cognitive, and visual abilities, providing tailored recommendations. By promoting safe driving practices and offering customized solutions, occupational therapy supports individuals in maintaining their independence and confidence behind the wheel, ultimately enhancing overall quality of life and community participation.
References and Further Reading
Key references include the Canadian Association of Occupational Therapists (CAOT) guidelines, the NZ Transport Agency’s resources, and the Assessment of Motor and Process Skills (AMPS). Additional reading materials are available through the Occupational Therapy Department of various hospitals and the Rookwood Driving Battery (RDB) documentation. For further details, visit idrivesafety.com.au or refer to the NZ Transport Agency’s factsheets. These resources provide comprehensive insights into driving assessments and rehabilitation programs.